About the sun & you
Healthy suntan? Certainly not!
The sun is the culprit for many of the aging signs of the skin, such as wrinkles, uneven pigmentation, skin laxity, and appearance of blood vessels underneath. After excessive exposure, there are a lot of free radicals floating around, damaging the skin functions, destroying the collagen, elastin, and skin matrix. More importantly, it can cause skin cancers! So it is a must to use sun-blocks to filter the harmful ultraviolet skin, in order to keep the skin healthy.
Sunlight consists of ultraviolet radiation, which can be divided into 3 sets of wavelengths:<
- UVA 320 - 400 nm
- UVB 290 - 320 nm
- UVC 100 - 290 nm

The two types of radiation that we should be careful of are UVA and UVB, since UVC is mostly absorbed in the upper atmosphere by the ozone layer of earth. However if it penetrates this valuable screening mechanism, it can cause grave cellular damage to tissue. UVA has a lower energy, but because of the longer wavelength, it can penetrate deeper into the skin and is responsible for the longer-term damages. UVB has a shorter wavelength but higher energy, and causes most of the sunburn. So when purchasing an sun-block, the formula need to be effective in blocking both UVA and UVB.
Skin Aging
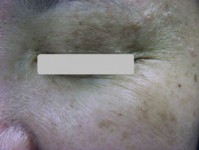
The aging signs on the surface of skin, including dry and rough skin, thin and transparent skin, loss of elasticity, wrinkles, dull skin tone, uneven pigmentation, are all very unattractive. Why do they happen when we age? These can be explained by two distinct types of aging.
Intrinsic (internal) aging : Aging caused by the genes we inherit
Extrinsic (external) aging : Aging caused by environmental factors, such as exposure to the sun.
 |
 |
Basic Biology of Skin
What is under the skin?
To understand further about the health of your skin, the first thing is to know your skin better, in terms of its structures and functions.
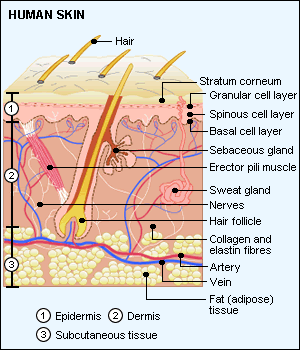
The skin is the largest organ of the body. It is soft, but elastic, can retain water inside the body, regulate the body temperature, and provide information of the outer environment. It comprises about 15% of the body weight. The total skin surface of an adult ranges from 12 to 20 square feet. In terms of chemical composition, the skin is about 70% water, 25% protein and 2% lipids.
Looking under the microscope, your skin can be divided into 3 main layers: Epidermis、Dermis and Subcutis,with connections to hair follicles, sebaceous glands sweat glands, nerves, blood vessels, lymph vessels and fine muscles of the hair follicles.
Sunscreens
Sun Protection Factors (SPF)
All sun-blocks will state their SPFs on the outside. Apart from the traditional sun-blocks, a lot of skin care products nowadays also add in some sun blocking ingradients to emaphsize their anti-photo-aging and whitening effect.
The SPFs can range from 10 to 100 or higher. The higher the figure, the longer it confers protection. It is a measure of after how much loger the skin will get a pre-determined “Minimum Redness” when the skin is exposed to a pre-determined strength of UVB, when compared to a control with no sun-block. A SPF of 15 means that the skin can stay 15 times longer under the sun before it will get the same damages.

Most sunscreens with a SPF of 15 or higher do an excellent job of protecting against UVB. Another way to look at it is in terms of percentages: SPF 15 blocks approximately 93 percent of all incoming UVB rays. SPF 30 blocks 97 percent; and SPF 50 blocks 99 percent. They may seem like negligible differences, but for someone who is sun-sensitive, or has a history of skin cancer, those extra percentages will make a difference.
However, no sunscreens, regardless of strength, should be expected to stay effective longer than two hours without re-application. Also, SPFs only reflect the protect against UVB, they do not have a direct relation to protection from UVA. Some sun-blocks do emphasise this factor by putting up a PFA (protection Factor for UVA) value, such as PA+++, the more + it has, the higher the protection.
Who Should Use Sunscreens?
Children under the age of six months should not be exposed to the sun. Anyone over the age of six months should use a sunscreen daily. Shade and protective clothings are the best ways to protect infants from the sun. Even those who work inside are exposed to ultraviolet radiation for brief periods throughout the day. Also, UVA is not blocked by glass windows.
What's in Sunscreens ?
There are 2 broad categories, most sunscreens use a mixture of both:

These are organic chemicals that can absorb certain ultraviolet wavelengths in the sunlight. They are in general water soluble, easy to use, and easy to conceal after application. The bad thing is very often they cause skin allergy or irritation. The higher the SPF, the more chemicals it contains, and the higher the chance of this problem.
| Common Ingredients | Filter |
|
Butyl Methoxy Dibenzoyl Methane (Avobenzone) |
UVA |
PABA has as much as 70% chance of causing allergic reaction, and is banned in some countries. Octyl Dimethy PABA can even release carcinogenic substances after irradiated by ultra-violet light. The Benzone group also frequently causes skin allergy as well as photo-sensitivity.
Reflective ElementsThey are minerals in composition, forming a layer on the skin to reflect out the ultra-violet lights. They do not cause skin allergy, but they make the preparations thick and sticky, so that it is obvious to have a white layer on the skin and not too comfortable after the application. Because of this, they are prone to block the pores and cause pimples.
| Common Ingredients | Reflect |
|
Titanium Dioxide |
UVA、UVB |
Attention When Buying and Using a Sunscreen
- A broad-spectrum sunscreen offering protection against both UVA and UVB should be used, with an SPF of 15 or higher.
- Apply plenty in order to get the SPF stated.
- Apply 30 minutes before sun exposure to allow the ingredients to fully bind to the skin.
- Apply again the same amount every two hours or immediately after swimming, toweling off, or sweating a great deal.
- Up to 40 percent of the sun's ultraviolet radiation reaches the earth on a completely cloudy day. So apply sunscreen even when on such a day out.
- Look at the ingredients if you have a history of skin allergy. Stop using it as soon as you notice the onset of irritation and write down the active ingredients, so that you can avoid it when buying again next time.
- If put direct under the sun for a long time, the effectiveness of sunscreens may be affected.
Skin Types and Sun Sensitivity
Dermatologists have a rating system, referred to as the Fitzpatrick Classification of Skin Types, to which skin is classified in its relationship to sensitivity to the sun.
| - Type I | Always burns and never tans (extremely sensitive) |
| - Type II | Always burns but sometimes tans (very sensitive) |
| - Type III | Sometimes tans but sometimes burns (sensitive) |
| - Type IV | Always tans but sometimes burns (minimally sensitive) |
| - Type V | Always tans and never burns (not sensitive) |
| - Type VI | Darkly pigmented brown or black skin (not sensitive to sunlight) |
In general, people with blond or red hair and a very pale and fair complexion, as well as blue or green eyes will fall within types I & II. Very often their ethnic ancestry can be traced back as Scottish, Irish, or Scandinavian.
People from the Mediterranean region, such as Italian, Greek and Spanish people, will normally fall within types III, IV.
Oriental Asian people can range from type III to IV. Northern region Chinese and Japanese are usually III, while Southern region Chinese, Vietnamese, Phillipinos etc are usually IV. East Asian such as the Indians, and Hispanic people would normally fall within type V. People from sub-Sahara Africa will fall under type VI.
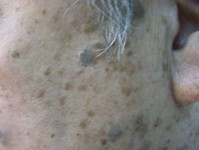
Photo-aging
Photo-aging is a technical term for the premature aging of the skin, caused by frequent unprotected exposure to sunlight. In the short term, damages include the usual sunburn, while long term damages includes unattractive skin changes as well as pre-cancer and cancer changes. The features of photo-damaged skin usually take the form of wrinkles, others include:
- Inelasticity and appearance of a thick leather
- Saggy and loose skin
- Dryness and roughness
- Uneven pigmentations
- Pigmented spots such as freckles
- Sallowness (yellowish discoloration)
Some recent studies have revealed various biochemical processes in the skin, whose end products are found to be responsible for photo-aging. One of these is Advanced Glycosylation End products (AGEs). These are formed by attachment of glucose and ascorbic acid to the long-lived proteins, such as collagen and elastin. AGES then cross link more proteins in the dermis irreversibly. Another is the singlet oxygen radicals ( free radicals ) which directly and indirectly cause damage to the inside structures of many cells.
Basic Biology of Skin
What is under the skin?
To understand further about the health of your skin, the first thing is to know your skin better, in terms of its structures and functions.
The skin is the largest organ of the body. It is soft, but elastic, can retain water inside the body, regulate the body temperature, and provide information of the outer environment. It comprises about 15% of the body weight. The total skin surface of an adult ranges from 12 to 20 square feet. In terms of chemical composition, the skin is about 70% water, 25% protein and 2% lipids.
Looking under the microscope, your skin can be divided into 3 main layers: Epidermis、Dermis and Subcutis,with connections to hair follicles, sebaceous glands sweat glands, nerves, blood vessels, lymph vessels and fine muscles of the hair follicles.

Skin Aging
The aging signs on the surface of skin, including dry and rough skin, thin and transparent skin, loss of elasticity, wrinkles, dull skin tone, uneven pigmentation, are all very unattractive. Why do they happen when we age? These can be explained by two distinct types of aging.
Intrinsic (internal) aging : Aging caused by the genes we inherit
Extrinsic (external) aging : Aging caused by environmental factors, such as exposure to the sun.
 |
 |
The Sun & You
Healthy suntan? Certainly not!
The sun is the culprit for many of the aging signs of the skin, such as wrinkles, uneven pigmentation, skin laxity, and appearance of blood vessels underneath. After excessive exposure, there are a lot of free radicals floating around, damaging the skin functions, destroying the collagen, elastin, and skin matrix. More importantly, it can cause skin cancers! So it is a must to use sun-blocks to filter the harmful ultraviolet skin, in order to keep the skin healthy.
Sunlight consists of ultraviolet radiation, which can be divided into 3 sets of wavelengths:<
- UVA 320 - 400 nm
- UVB 290 - 320 nm
- UVC 100 - 290 nm

The two types of radiation that we should be careful of are UVA and UVB, since UVC is mostly absorbed in the upper atmosphere by the ozone layer of earth. However if it penetrates this valuable screening mechanism, it can cause grave cellular damage to tissue. UVA has a lower energy, but because of the longer wavelength, it can penetrate deeper into the skin and is responsible for the longer-term damages. UVB has a shorter wavelength but higher energy, and causes most of the sunburn. So when purchasing an sun-block, the formula need to be effective in blocking both UVA and UVB.

